Adrenal Adenoma: What Every Patient Should Know
The adrenal glands produce hormones which help to maintain homeostasis.¹ Hormone production can be impacted by the presence of a tumor. A common way tumors of the adrenal gland may be detected is through imaging studies.²
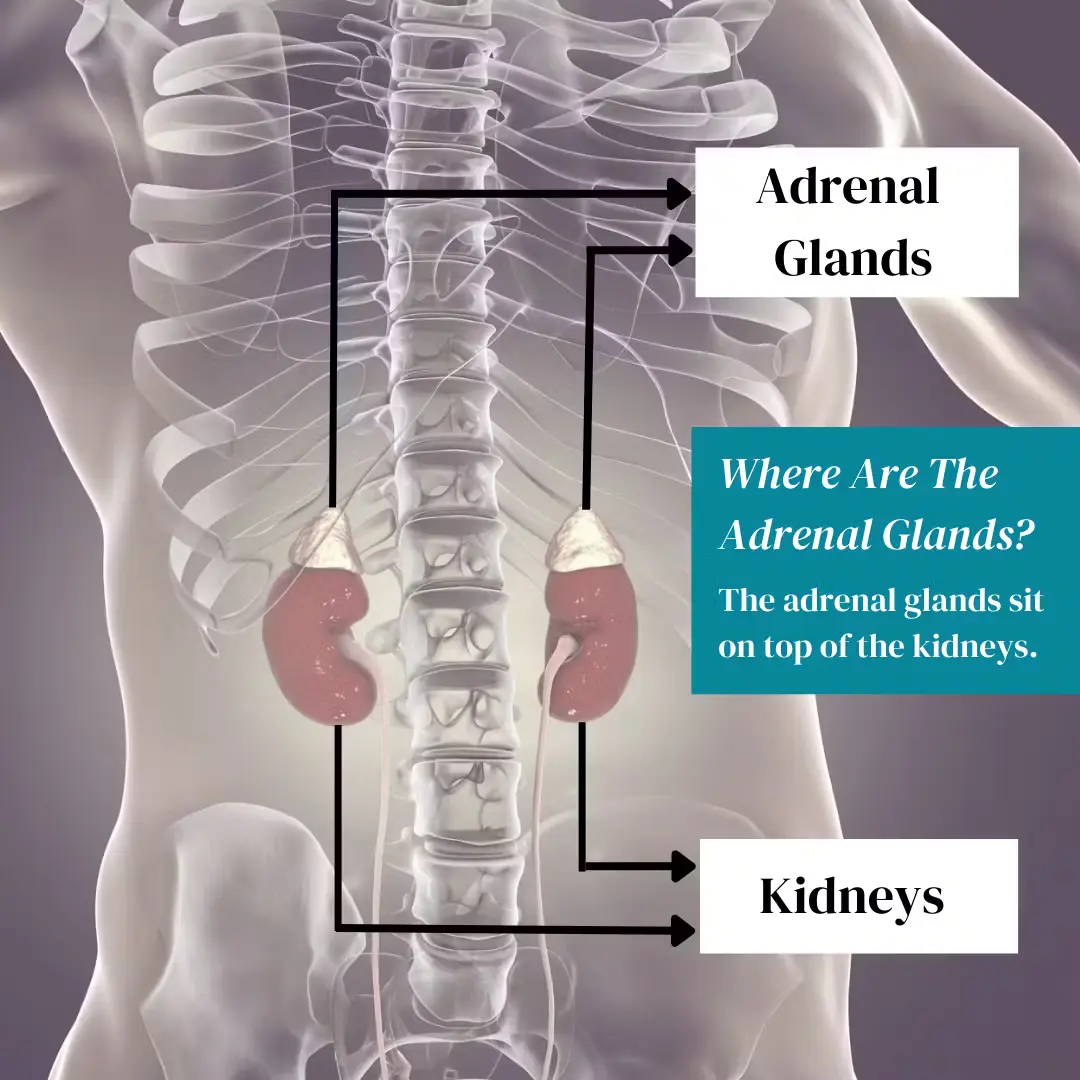
What Do The Adrenal Glands Do?
The adrenal gland is part of the HPA axis and produces hormones that help to regulate metabolism, the immune system, blood pressure, and other essential functions.¹
What Is An Incidentaloma?
An adrenal incidentaloma is a tumor that is found on one or both of the adrenal glands “by accident” or “incidentally” when an imaging study, like a CT scan or MRI, is done for other medical reasons.²
If an adrenal incidentaloma is found, the doctor will determine if it is a benign tumor or malignant tumor. Most adrenal gland tumors are benign, but malignancy is diagnosed in 6-8% of patients with adrenal tumors.² The characteristics of the tumor in the imaging study is valuable in differentiating between a benign and malignant process.⁹
Once malignancy is ruled out, the health care provider will likely try to determine if the incidentaloma is abnormally secreting excess hormones.²
Adrenal Gland Adenoma: Functioning or Not?
Adrenal gland adenomas can be categorized as functioning or non-functioning.² However, it is estimated that 15% of adrenal gland adenomas may be functioning and produce hormone excess.³
Non-Functioning Adrenal Gland Adenoma
A non-functioning tumor means that the nodule is not overproducing or secreting an abnormal amount of adrenal hormone.³
Functioning Adrenal Gland Adenoma
A functional tumor abnormally produces and secretes a higher amount of one or more of the numerous adrenal hormones.³
Related: Could You Have A High Level Of Cortisol? What Every Patient Needs To Know
Cortisol is the hormone that helps the body respond to situations of physical or severe emotional stress. The human body needs cortisol to survive, but prolonged exposure to too much cortisol may lead to a condition known as Cushing syndrome.⁷ Cushing syndrome results in a constellation of clinical signs and symptoms.⁵ Patients with Cushing syndrome may develop overt symptoms such as easy bruising, muscle weakness, facial swelling and redness, unexpected body hair (hirsutism), and stretch marks. Some less obvious symptoms patients may develop include high blood sugar, weight gain, abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, insomnia, acne, severe fatigue, disturbances in sex drive, and irregularities in the menstrual cycle.⁴
While there are many screening tests that may be recommended if the doctor suspects Cushing syndrome, all patients with adrenal incidentalomas are recommended to be screened using the 1-mg Dexamethasone Test (DST).⁶
Dexamethasone Suppression Test (DST)
Even without obvious symptoms of Cushing syndrome, cortisol excess can be present with an adrenal incidentaloma. Therefore, testing for abnormally high levels of cortisol is important in all patients with adrenal incidentalomas.²
The dexamethasone suppression test is the standard initial test to determine whether there is excess cortisol secretion in the adrenal tumor. It is also called the low dose dexamethasone suppression test because 1 mg of dexamethasone is taken orally by the patient.⁴,⁶
If a patient is asked to take the dexamethasone suppression test, he or she will be instructed to take 1 mg of oral dexamethasone between 11 PM and midnight. Then, between 8 AM and 9 AM the next morning, the patient’s blood should be drawn.⁴
The dexamethasone pill mimics cortisol in the body. This should signal the body to know that there is already cortisol in the system and the body should lower the natural production of cortisol.⁸ Blood is drawn at 8 AM the next day to measure the cortisol levels when they should be at their lowest. If the test is not performed correctly, your doctor may need you to repeat it.
To obtain an accurate reading, your doctor will need to make sure that the conditions are appropriate. Some factors that may result in a false positive would be if you are experiencing any acute illness or stress. Use of estrogen, such as birth control pills, may lead to a false positive and use of other medications may also lead to incorrect results.
The dexamethasone suppression test is the standard initial test to determine whether there is excess cortisol secretion in the adrenal tumor. It is also called the low dose dexamethasone suppression test because 1 mg of dexamethasone is taken orally by the patient.⁴

Adrenal Gland Tumors: Take Home Points
When an adrenal nodule or tumor is incidentally found during imaging, usually for another and unrelated reason, further work up is needed.² An endocrinologist is an expert in hormone science and is the best expert to evaluate this. The evaluation includes a thorough medical history, review of signs and symptoms, and review of the imaging characteristics of this nodule. A 1-mg DST is recommended for all patients with an adrenal incidentaloma.²,⁶
We discuss products we think are useful to people. If you buy something through our links, we may earn a commission. Remember to check with your personal physician to see if a product recommended is right for you.